Secure your place at the Digiday Publishing Summit in Vail, March 23-25

One thing became clear this year: AI platforms are changing where, how and how much referral traffic gets sent to publishers’ sites.
It’s a topic we covered often this year. ChatGPT referral traffic nearly doubled, but is still a very small percentage of publishers’ overall traffic. Google’s AI Overviews, its AI-generated summaries on the search page, reduced click-through rates across more search queries. And as the year comes to a close, publishers are figuring out how to maintain brand visibility in AI search.
The five graphs below illustrate where AI referrals stand today — which platforms are gaining share, sending traffic and driving conversions. Together, they reveal a new audience pipeline forming outside of traditional search and social platforms, giving a preview of next year’s competitive landscape for publishers.
Gemini referral traffic surges, but ChatGPT still reigns supreme
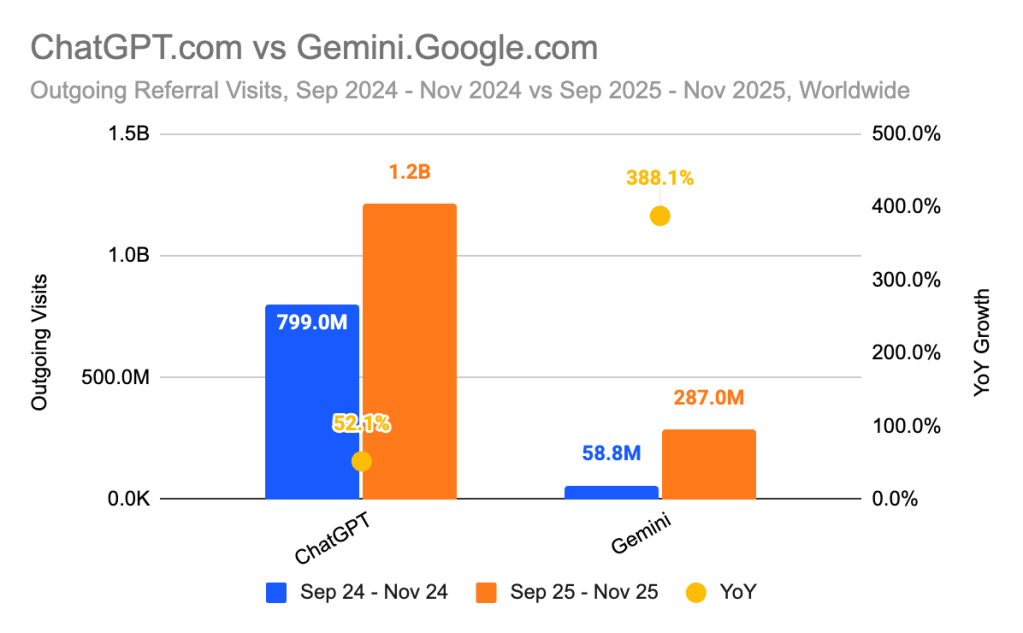
Despite the dominance of OpenAI’s ChatGPT in the volume of referral traffic the AI tool is sending to other sites, Google’s Gemini is catching up. From September to November 2025, ChatGPT referrals increased 52% year over year. Gemini referral traffic, on the other hand, grew 388% in that same time period, according to data from Similarweb shared with Digiday.
That’s likely because more people are using Gemini. Between August and November, Gemini’s global desktop visits doubled, while ChatGPT’s rose about 1% over the same period, according to data from research firm Sensor Tower, which tracks 5 million consumers globally. Gemini released a new image generation model, Nano Banana, and its Gemini 3 update in that time, likely drove increased adoption of the AI tool.
Gemini’s monthly active users increased about 30% to 346 million, while ChatGPT’s rose about 5% to 810 million, according to the data.
AI platforms are only driving 1% of overall traffic
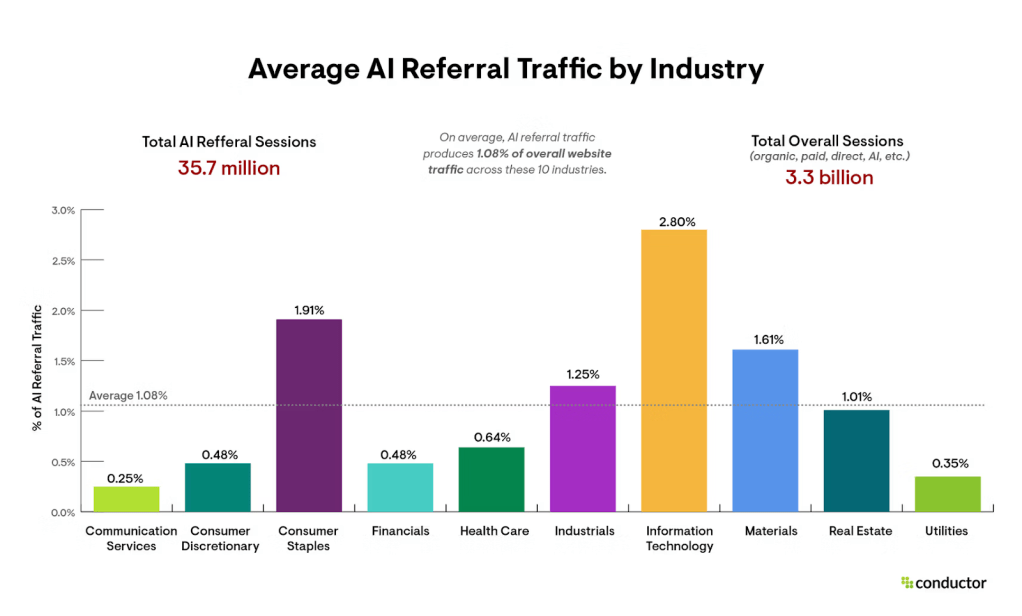
Despite AI platforms’ growing user base and increase in referral traffic to external sites, the overall percentage of referrals they’re sending is minuscule.
AI platforms are only driving an average of 1% of overall web traffic across 10 major industries, according to data by AEO and SEO marketing platform Conductor. As Digiday reported in July, referral traffic from AI platforms like OpenAI’s ChatGPT and Perplexity still isn’t enough to offset the decline in search-driven visits.
ChatGPT remains the main driver of AI referral traffic. According to Conductor, 87.4% of all AI referral traffic across these 10 key industries comes from ChatGPT, on average. (That does not include traffic from Google’s AI Overviews or AI Mode, but does include traffic from Gemini, ChatGPT, Copilot, Perplexity and Claude).
Users less likely to click on a link with an AI summary
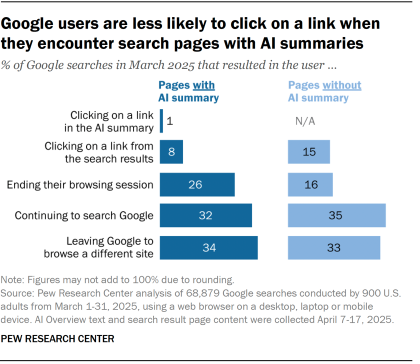
Google users are less likely to click on a link when they see an AI summary on a search page, according to data from Pew Research Center. That explains why some publishers have told Digiday their clickthrough rates on Google have all but disappeared since Google introduced AI Overviews last year.
Users who saw an AI summary clicked on a traditional search result link in 8% of all visits. Those who did not encounter an AI summary clicked on a search result nearly twice as often (15% of visits), according to Pew Research Center.
For what it’s worth, Google refutes these findings, continuing to state that people are searching more and asking more complex queries with AI Overviews. Google also says people see more links on its search results page with AI Overviews, giving sites more opportunities to get referral traffic – though most publishing execs vehemently disagree.
“No company drives more value to the web than Google, and we send billions of clicks to websites every day,” a Google spokesperson told Digiday. “As technology and people’s information needs evolve, we’re building our products to highlight the web and launching new features like Preferred Sources to help connect people with the sites they value.”
But AI referrals drive higher conversions
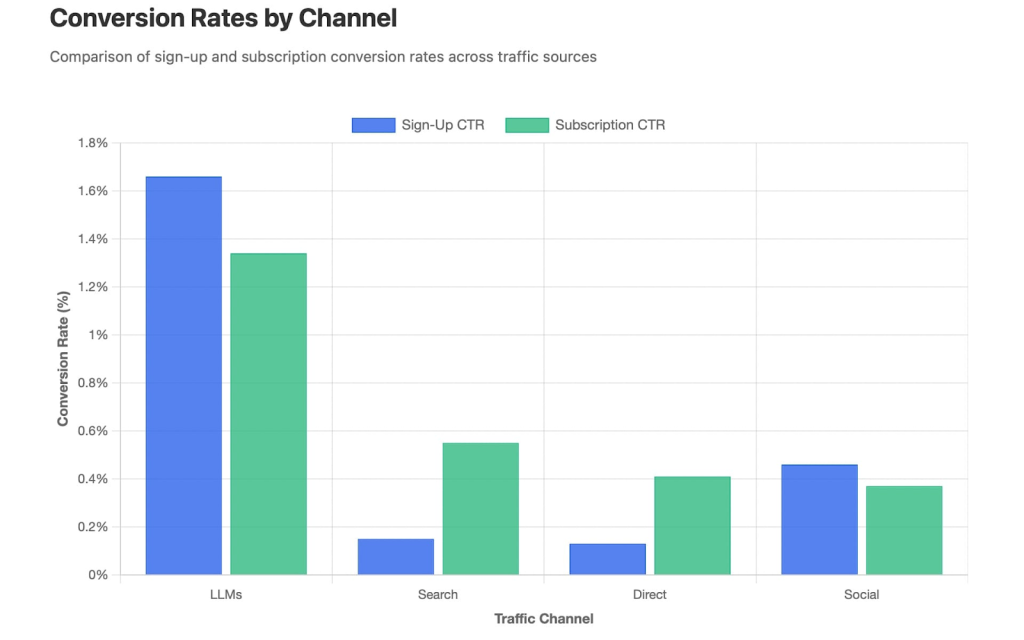
So far, these graphs may be painting a grim picture of the impact AI platforms are having on referral traffic. But there are some bright spots.
For example, Microsoft Clarity analyzed over 1,200 publisher and news websites and found that conversion rates (such as sign-up and subscription conversions) were notably higher when people came via LLMs, compared to search, direct or social channels.
The study shows that site visitors coming from LLMs converted to sign-ups at 1.66%, compared to 0.15% from search, 0.13% from direct traffic and 0.46% from social media. It was a similar story for subscription conversions, with LLM traffic converting at 1.34%. Search converted subscribers at a rate of 0.55%, direct traffic at 0.41% and social media at 0.37%
AI tools crawl way more than they’re refer
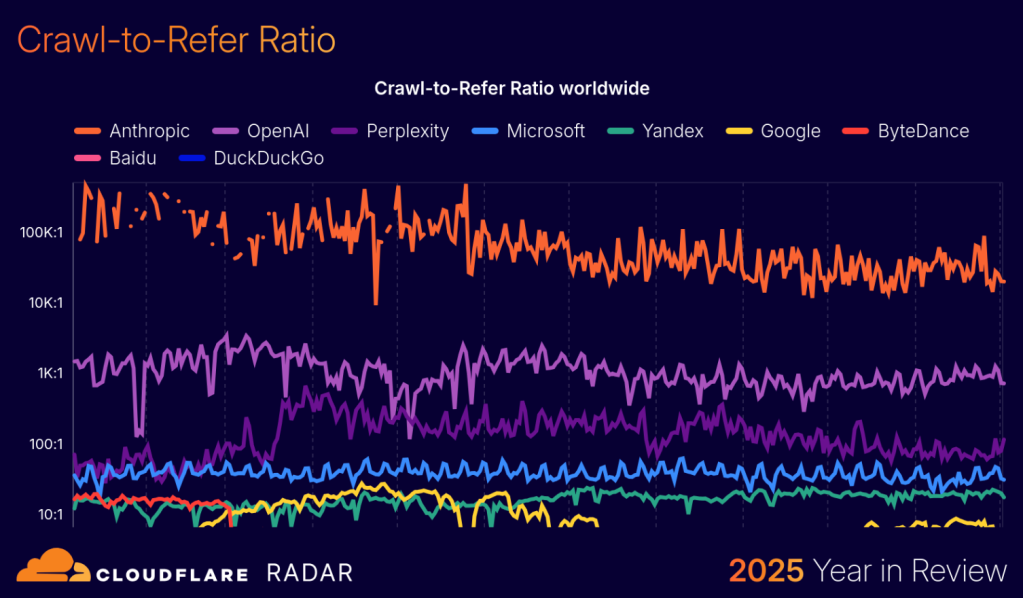
Our last graph shows the crawl-to-refer ratio of AI tools this year, a metric that CDN and cybersecurity provider Cloudflare began tracking this summer to monitor how often an AI or search platform was sending traffic to a site compared to how often it crawls that site for information.
Anthropic had the highest crawl-to-refer ratios this year, reaching as much as 500,000:1 – meaning its AI crawling was scraping sites at a rate far greater than it was sending real people to sites. OpenAI’s ratios, in comparison, reached a peak of 3,700:1 in March.
Cloudflare’s “Radar Year in Review” report suggested ChatGPT’s crawl-to-refer ratio may have stabilized after that because more people used the tool for search this year, which includes links back to source websites in its AI-generated responses. More people clicking on those links would increase the referrer counts, and possibly lower the ratio – if crawl traffic wasn’t increasing at a similar or greater rate, according to the report.
Perplexity had the lowest crawl-to-refer ratios of the major AI platforms, spiking in late March above 700:1. That’s interesting, considering publishing execs have told Digiday this year that its AI crawler is one of the most badly-behaved (this could be because Perplexity is using headless browsers to scrape, though Perplexity denies this).
Meanwhile, Cloudflare found that the crawl volume of Googlebot, Google’s AI crawler that scrapes for both search engine indexing and AI training, dwarfed that of other major AI bots. Googlebot originated 4.5% of HTML content requests this year, a share slightly larger than AI bots in aggregate. And AI “user action” crawling, which tracks website visits in response to user queries in an AI chatbot, increased by over 15-times in 2025, according to Cloudflare.
More in Media

Media Briefing: As AI search grows, a cottage industry of GEO vendors is booming
A wave of new GEO vendors promises improving visibility in AI-generated search, though some question how effective the services really are.

‘Not a big part of the work’: Meta’s LLM bet has yet to touch its core ads business
Meta knows LLMs could transform its ads business. Getting there is another matter.

How creator talent agencies are evolving into multi-platform operators
The legacy agency model is being re-built from the ground up to better serve the maturing creator economy – here’s what that looks like.







